- Value Objects
- A value object is defined by it’s attributes
- Two value objects are equivalent if their attributes are the same.
- Value Objects are immutable
- in addition to state, value object can contain business logic.
- Messages in Reactive Systems are implemented as value objects.
- Entities
- An Entity is defined by a unique identity
- An Entity May change its attributes but not its identity.
- If the Identity changes, it is a new entity regardless of it’s attributes.
- Entities are the single source of truth for a particular id.
- Entities can also Contain business logic
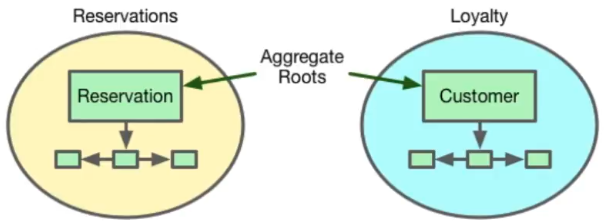
- Aggregates
Aggregate is a specific type of Entity
- An Aggregate is a collection of domain objects bound to a root entity.
- The root entity is called the Aggregate root.
- Objects in an aggregate can be treated as a single unit.
- Access to objects in the aggregate must go through the aggregate root.
- Transaction should not span multiple Aggregate Roots.
- Aggregates are good candidates for distribution in a Reactive System.
- Determining the Aggregate Roots
- Choosing an aggregate root is not always straightforward.
- the aggregate root can be different from one context to another.
- some contexts may require multiple aggregate roots.
- some questions to consider:
- is the entity involved in most operations in that bounded context?
- if you delete the entity, does it require you to delete other entities?
- will a single transaction span multiple entities?