-
What is the iterator pattern?
-
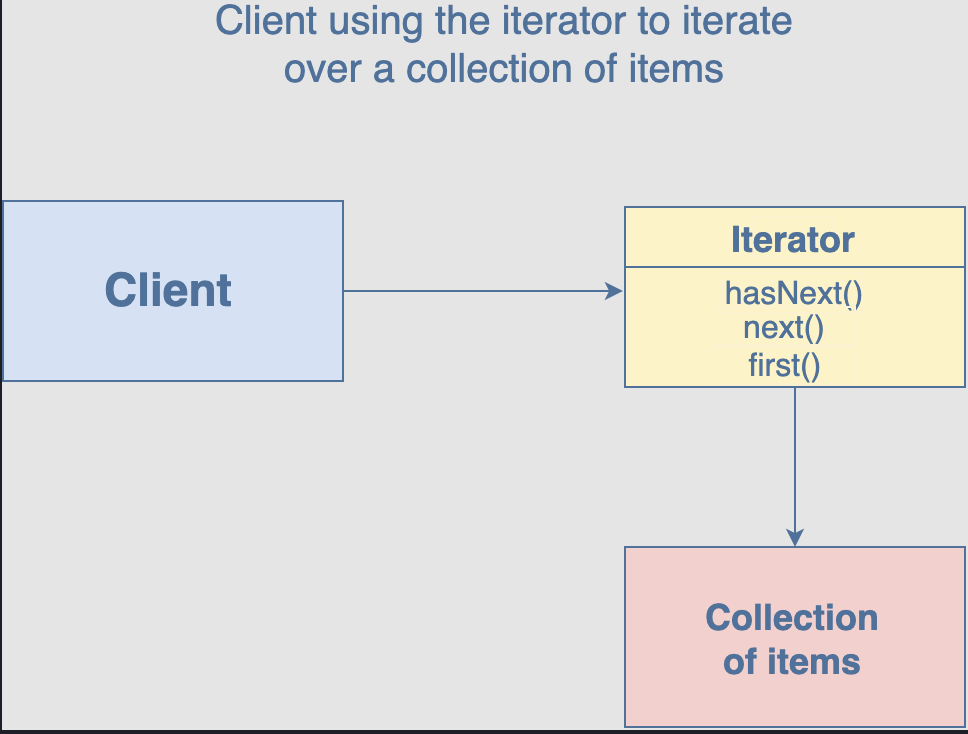
The iterator pattern allows the definition of various types of iterators that can be used to iterate a collection of objects sequentially without exposing the underlying form.
-
Iterators encapsulate how the traversal occurs in an iteration. Most languages have built-in iterators such as IEnumerable and IEnumerator. However, JavaScript only supports basic looping constructs like for loop, for-in loop, while loop etc. The iterator pattern allows JavaScript developers to build other complex iterators which can be used to easily traverse collections that are stored in something complex such as graphs or trees. These iterators can then be used by the client to traverse a collection without having to know their inner workings.
-
Iterators follow the behaviour where they call a next function and step through a set of values until they reach the end. To do this, they need to maintain a reference to the current position as well as the collection they are traversing. Hence, an iterator has functions such as next,_ hasNext_,_ currentItem_, and_ each_
- It presents a way to access the elements of an object without exposing the underlying presentation.
- Wikipedia says
In object-oriented programming, the iterator pattern is a design pattern in which an iterator is used to traverse a container and access the container’s elements. The iterator pattern decouples algorithms from containers; in some cases, algorithms are necessarily container-specific and thus cannot be decoupled.
-
When to use the iterator pattern?
-
This pattern can be used when dealing with problems explicitly related to iteration, for designing flexible looping constructs and accessing elements from a complex collection without knowing the underlying representation. You can use it to implement a generic iterator that traverses any collection independent of its type efficiently.